Filtering methods.
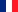
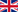
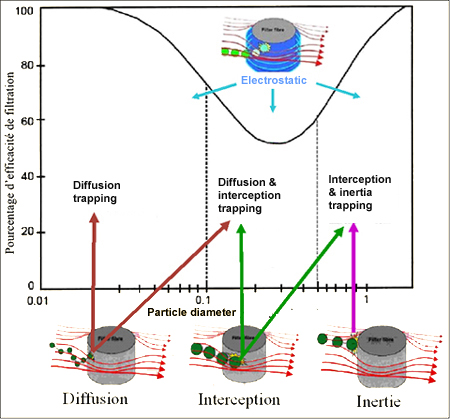
With "nano" dimensions, particles interact with fibers following two mechanisms:
- trapping by diffusion: the random movements of air molecules make these very small particles (without inertia) roam through direct current lines until they come into contact with a fiber,
- electrostatic attraction (non-specific to “nano”): the charged particles are attracted to fibers with an opposite charge. The electrostatic attraction is highly effective until saturation of filter or charge neutralization.